


Reperfusion is beneficial up to 12 hours after the onset of symptoms. Reperfusion therapy should be initiated as quickly as possible by preferably primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or fibrinolysis. Initial treatment of STEMI is relief of ischemic pain, stabilisation of hemodynamic status and restoration of coronary flow and myocardial tissue perfusion. ST-segment elevation Myocardial Infarction ĭepending on the (working) diagnosis STEMI or NSTE-ACS, the revascularisation strategy varies. ß blockers lower heart rate and blood pressure, to decrease the oxygen demand of the heart. The treatment of ACS also focuses on medication to reduce the workload of the heart. Aspirin and the P2Y12 receptor blocker are both platelet aggregation inhibitors. All patients diagnosed with ACS should start with aspirin and a P2Y12 receptor blocker (clopidogrel, prasugrel or ticagrelor). The thick arrow indicates the preferred strategy.Īs the formation of an intracoronary thrombus is a central mechanism in ACS and (recurrent) subsequent outcomes, the cornerstone in the treatment of ACS is antithrombotic treatment. More information abou the ECG during myocardial infarction can be found on ECGpedia. Left main coronary artery ischemia – Lead aVR.Inferior wall ischemia - Leads II, III, and aVF.Apical or lateral ischemia - Leads aVL and I, and leads V4 to V6.
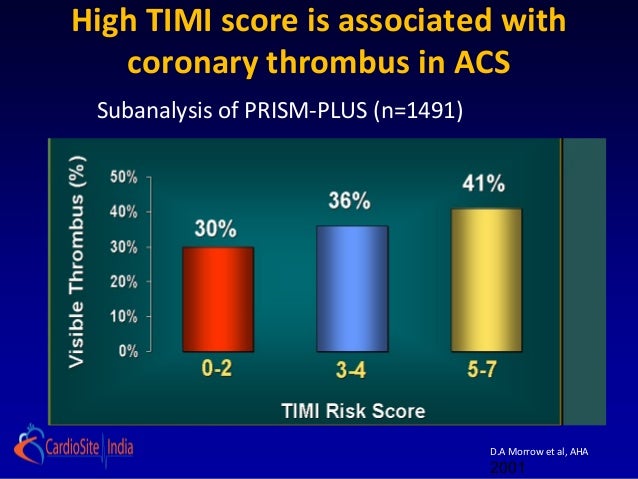
#Timi score wiki indication for early invasive serial
Therefore it is important to make serial ECGs, certainly if a patient has ongoing symptoms. However, a single ECG may not reflect the dynamic pathophysiology of the ACS. The ECG is an important and easy modality which can assist in the diagnosis and prognostication of ACS. Īn electrocardiogram (ECG) should be made on arrival in every patient with suspected ACS. In more stable ACS patients, history and physical examination are helpful to exclude other causes of chest pain, such as aortic valve stenosis, aorta dissection, arrhythmias, pulmonary embolism, pneumonia, heartburn, hyperventilation or musculoskeletal problems. įurthermore, signs of heart failure are important, such as pulmonary crackles during auscultation and pitting oedema of the ankles. The focus of the physical examination should be to recognize signs of systemic hypoperfusion such as hypotension, tachycardia, impaired cognition, pale and ashen skin. Symptoms of heart failure such as orthopnea (dyspnoea when lying flat), progressive dyspnoea and peripheral oedema are indicative of the extent of the problem. diabetes mellitus, current smoking, hypertension, hyperlipidemia) and family history (first degree relatives with myocardial infarction before the age 55 of (males) or 65 (females) and/or sudden cardiac death). It is important to complete the medical history (prior history of ischemic events or vascular disease), risk factors for cardiovascular disease (a.o. Some patients including elderly and diabetics may present with aspecific symptoms. Shortness of breath can occur, as well as sweating, fainting, nausea and vomiting, so called vegetative symptoms. Frequent accompanying symptoms include a radiating pain to shoulder, arm, back and/or jaw. The pain does not decrease at rest and is only temporarily relieved with nitroglycerin. The most typical characteristic of an ACS is acute prolonged chest pain. Troponine definitely classifies into myocardial infarction (damage) or not. The ECG classifies into ST elevtion or not. Different terminology is used during different phases of the chest pain workup.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
